Device Infield Update (OTA) Guide¶
Guide to implementing support for device in-field firmware / application updates (OTA - Over The Air) using the Murano platform IoT Connectors and ExoSense.
implementation of remote infield update of software, firmware, and applications requires support in the IoT edge device. The tools and schema provided by Exosite were support to enable any type of edge device from resource constrained embedded microcontrollers to industrial computers.
Edge developers must ensure secure API communication and provisioning is used and handle proper firmware update handling for failover.
Requirements¶
| Requirement | Notes |
|---|---|
| Device has an Internet Connection (IP) | The device must have a public internet connection for use with Exosite's standard Murano platform. (Contact support for device cloud integrations) |
| Device supports MQTT and/or HTTP protocol | When using MQTT for device API, HTTP is required to download actual content files |
| Device supports TLS Security | The TLS encryption requirement can be turned off for development, but not to be used for production use cases. |
| An Exosite Platform Account | To create IoT Connectors, an Exosite Account is required with ExoSense deployed. |
| Existing IoT Connector & ExoSense | For purposes of this guide, it is assumed the device already is connected and sending data. Connect a Device Guide |
OTA Update Schema
The Exosite OTA Update Schema has the full set of details for the infield update interface.
IoT Connector Setup¶
ExoSense requires and uses the following resources. Having used the Standard ExoSense Connector Template, these should already be set up. For the purposes of OTA updates, the following resources are used.
| Resource Name | Writer | Description |
|---|---|---|
config_otau | Device / App | Used by the application / platform to let a device know a software package is available for OTA process. See OTAU Schema |
otau_in | Device | Used by device to send status updates for the OTA process. See OTAU Schema |
Protocol Support¶
Devices can communicate with the defined resources using HTTP or MQTT device protocol.
Downloading Content over MQTT Port
For constrained devices that may only have one network port, the downloading of content is handled through HTTP. If the device is using MQTT and content files for downloading are stored in Murano, the device will need to switch to HTTP for downloading. Information about switching from MQTT to HTTP for download can be found here. Content Over MQTT port
When using HTTP, the device should poll periodically (or use long-polling) for the config_otau resource. When using MQTT, a topic subscription for the resource config_otau would be used.
Software Package Manifest¶
The OTAU process uses the concept of a manifest which specified information about the software package for updating the device firmware, application, etc. This allows flexibility for both resource constrained embedded products and industrial computers running multiple application processes.
This manifest is a JSON blob that is written to the config_otau resource by the application, platform, or API to let the device know it has updates.
Software Package Manifest contents
| Key | Required? | Description |
|---|---|---|
version | Required | used to distinguish this OTAU from others (eg. version number). |
name | Required | human-readable name of OTAU (eg. “Security Update”) |
description | Optional | description of OTAU |
type | Required | used by the gateway to determine how to handle the OTAU |
payload | Required | Depends on the type |
An example of a Software Package manifest
{
"version": "1.2.0",
"name": "Firmware upgrade",
"description": "Updates to main application and protocol handlers",
"type": "URL_LIST",
"payload": [
"http://example.com/file1",
"http://example.com/file2",
"http://example.com/file3"
]
}
Software Payload Files
The Manifest information defines the payload of file/file locations to be downloaded. These files need not be stored in Exosite's IoT Connector content. They can be, but can point to any location your device has access to.
A file included in the payload may simply be a set of instructions for applying commands for updates.
Files that are stored in the Exosite IoT Connector will not have a host as part of the URL.
Software Package Creation¶
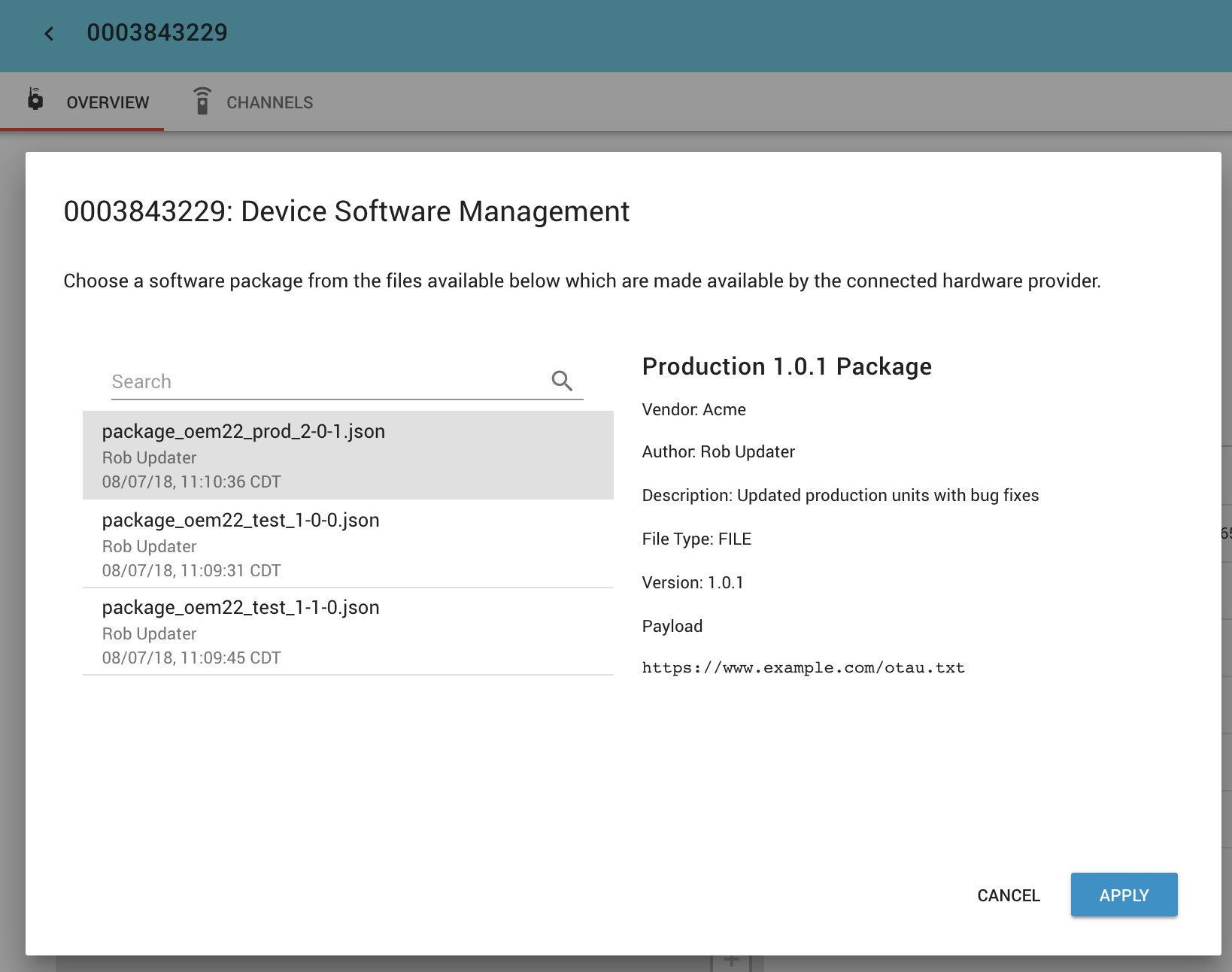
ExoSense will list Software Packages that are associated to specific devices. This can be done through the ExoSense UI.
Software Package Role Permission
To create software packages, the user's role must include the Device Software Package Administration permission.
ExoSense Software Package UI¶
To list a software package for one or more devices, the package can be created in the ExoSense application using the SOFTWARE PACKAGES tab on the devices page. When creating a new package, a form allows you to specify the information that goes into the manifest. The ExoSense software package UI provides two options, either files or links - both with the package type 'URL_LIST'.

When submitting the new software package, the package is made available to users of the specified devices.
Important: The software package is not automatically applied to the devices.
Software Package of Uploaded Files¶
Uploaded files are placed in the Exosite IoT Connector content area to allow devices to download.
The device firmware should recognize that payload items without a full host as files stored in the IoT Connector. The Device HTTP protocol can be used to download these files.

Example config_otau manifest
{
"version": "1.0.2",
"name": "Firmware update",
"description": "firmware package updated",
"type": "URL_LIST",
"payload": [
"firmware_updatev102.txt"
]
}
Software Package of Links¶
A software package can be one ore more links. In this use case, the device uses this links of URL links to download / fetch the files and then apply them.

Example config_otau manifest
{
"version": "08-14-2021",
"name": "Update Device Packages 08-14-2021",
"description": "",
"type": "URL_LIST",
"payload": [
"https://mycontentserver.com/file1",
"https://mycontentserver.com/file2"
]
}
ExoSense API¶
Software packages can be created and uploaded using the ExoSense API. If storing content in the IoT Connector, an initial call should be made to create the content and upload the files. Then make the call to create the empty content file to store the proper package information.
ExoSense GraphQL API Example to create Software Package
[
{
"operationName": "CreateContentGQL",
"variables": {
"content": {
"name": "package_oem_firmware_update_1.0.1.json",
"content_type": "firmware",
"type": "firmware",
"length": 205,
"tags": [
{
"name": "otau_info",
"value": "{\"author\":\"user@example.com\",\"product\":\"myconnector\",\"config_otau\":{\"version\":\"1.0.1\",\"name\":\"firmware update\",\"description\":\"firmware update\",\"type\":\"URL_LIST\",\"payload\":[\"firmware_updatev101.txt\"]}}"
},
{
"name": "pid",
"value": "d1zzd6dflnt50000"
},
{
"name": "total-devices",
"value": 3
},
{
"name": "d1zzd6dflnt50000.a0001",
"value": "1"
},
{
"name": "d1zzd6dflnt50000.a0002",
"value": "1"
},
{
"name": "d1zzd6dflnt50000.a0003",
"value": "1"
}
],
"product_id": "d1zzd6dflnt50000"
}
},
"query": "mutation CreateContentGQL($content: ContentInput) {\n createContent(content: $content) {\n id\n url\n inputs\n method\n field\n enctype\n __typename\n }\n}\n"
}
]
The response will include information for uploading the content file to storage.
Device OEM - Murano IoT Connector Content¶
ExoSense stores and retrieves the information about the software package (the manifest) in empty content files in the IoT Connector, placing the config_otau information in a tag (otau_info) associated to this empty content file.
To use the Murano CLI to upload software packages, please contact support for more information.
Device OTAU Interface¶
Manifest (config_otau)¶
When the application / platform side has a new software package for a device the config_otau resource is written to with information (i.e. a manifest) about the software package. A device will read this (polling or subscription) to know the software is available with information on what to download.
Status Updates (otau_in)¶
Once a device begins the OTAU process, it can provide status updates to the platform / application by writing to the otau_in resource.
Flow¶
The basic steps for the device implementation are as follows:
- Subscribe (MQTT) or poll (HTTP) the 'config_otau' resource to be notified of a new manifest for the software package. Be sure to acknowledge the information contained in
config_otauby writing the value back. - The 'payload' defines the content files to download.
- Download the necessary files of the software package manifest. Note that files may simply be instructions for upgrading.
- Install / Update local firmware / packages / applications with these files.
- During this process, provide updates to ExoSense for end-users to see using the
otau_inresource and the defined states in the OTAU schema. - When completed, send one last status update that contains the status
INSTALLED_VERSION.

Example Python Script showing OTAU Flow
import json
import http.client as client
import base64
import hashlib
import urllib.parse
import ssl
import time
# EXAMPLE TO DEMONSTRATE THE EXOSITE / EXOSENSE INFIELD UPDATE (OTAU) PROCESS
# THIS EXAMPLE USES HTTP DEVICE PROTOCOL
# IF USING A CONSTRAINED DEVICE WITH ONE PORT WITH MQTT, SEE COMMENTED OUT CODE FOR USING
# HTTP DOWNLOADS OVER A MQTT PORT USING THE ALPN PROTOCOL
# MORE INFO ON ALPN: https://docs.exosite.io/device-connectivity/device-http-api/#content-over-mqtt-port
product_id = "<PRODUCT_ID_HERE>" # IOT CONNECTOR PRODUCT (IOT CONNECTOR) ID USED IN <PRODUCT_ID>.M2.EXOSITE.IO
token = "<DEVICE_TOKEN_HERE>" # ASSUMED DEVICE HAS ACTIVATED AND HAS TOKEN LOCALLY STORED
# IF USING MQTT - If not using HTTP over the MQTT port, this is not required.
# Use port 8883 for MQTT, could be changed to port 443 if configured from Murano product settings
# This is the important option enabling use of HTTP over MQTT port
# def ssl_alpn():
# try:
# print(f"OpenSSL version:{ssl.OPENSSL_VERSION}")
# ssl_context = ssl.create_default_context()
# alpn_protocols = ['http/1.1']
# ssl_context.set_alpn_protocols(alpn_protocols)
#
# return ssl_context
# except Exception as e:
# print("Exception in ssl_alpn()")
# raise e
# context = ssl_alpn()
# host = f"{product_id}.m2.exosite.io:8883"
# conn = client.HTTPSConnection(host, context=context)
# IF ONLY USING HTTP protocol
host = f"{product_id}.m2.exosite.io"
conn = client.HTTPSConnection(host)
conn.set_debuglevel(0) # SET HIGHER TO SEE HTTP COMMUNICATION DETAILS
print("OTAU: Application starting")
def update_otau_status(status):
## Update otau status
endpoint = f"/onep:v1/stack/alias"
headers = {
'X-Exosite-CIK': token,
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=utf-8',
}
otau_status_string = json.dumps(status)
status_body = urllib.parse.urlencode({'otau_in': otau_status_string})
conn.request('POST', endpoint, body=status_body, headers=headers)
r = conn.getresponse()
#print(f"STATUS: {str(r.status)}\nREASON: {r.reason}")
r.read()
# Not handling responses for connection handling, etc in this example
while True:
print("OTAU: Waiting for new OTAU commands via config_otau")
##
## Begin polling config_otau resource for new update command
##
endpoint = f"/onep:v1/stack/alias?config_otau"
headers = {
'X-Exosite-CIK': token,
'Accept': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=utf-8',
'Request-Timeout': 300000,
'If-Modified-Since': 0
}
conn.request('GET', endpoint, headers=headers)
r = conn.getresponse()
#print(f"STATUS: {str(r.status)}\nREASON: {r.reason}")
if r.status == 200:
# New Value
resp_headers = r.getheaders()
for header in resp_headers:
if header[0] == "Last-Modified":
print(header)
#last = 0
#last = int (time.time())
data = r.read()
#print(data)
bodyparams = urllib.parse.parse_qs(data)
update_manifest = bodyparams[b'config_otau'][0]
print("OTAU: New Update found!")
##
## ACK Back by writing this value back to the platform
## Note: This could be done 'after' doing the infield update incase of power / update process failures
##
endpoint = f"/onep:v1/stack/alias"
headers = {
'X-Exosite-CIK': token,
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=utf-8',
}
ackbody = data
conn.request('POST', endpoint, body=ackbody, headers=headers)
r = conn.getresponse()
#print(f"STATUS: {str(r.status)}\nREASON: {r.reason}")
r.read()
##
## Parse Manifest and do Infield Update process
##
manifest = json.loads(update_manifest.decode('UTF-8'))
print(f"OTAU: Manifest Information:\n Name: {manifest['name']} \n Version: {manifest['version']} \n Type: {manifest['type']} \n Payload: {manifest['payload']} ")
## Update otau status
update_otau_status({'version': manifest['version'],'status': 'INIT' ,'message': ''})
##
## Downloading payloads
## Note, if the type is URL_LIST and files do not contain a host, assume content is in Exosite IoT Connector for content to download
##
time.sleep(3)
print(f"OTAU: Downloading Packages...")
## Update otau status
update_otau_status({'version': manifest['version'],'status': 'DOWNLOAD' ,'message': ''})
## <DOWNLOAD CODE HERE>
if manifest['type'] == "URL_LIST":
print(f"OTAU: begin downloading files from URL List")
for item in manifest['payload']:
print(f"OTAU: Software File - {str(item)}")
# ASSUMES CONTENT IN EXOSITE IoT CONNECTOR CONTENT BUT COULD BE HOSTED ANYWHERE WITH FULL HOST / URL in URL LIST
endpoint = f"/provision/download?id={str(item)}&info=true"
headers = {
'X-Exosite-CIK': token,
'Accept': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=utf-8',
}
conn.request('GET', endpoint, headers=headers)
r = conn.getresponse()
#print(f"STATUS: {str(r.status)}\nREASON: {r.reason}")
content_blob = r.read()
content_info = content_blob.decode('UTF-8').split(",")
print(f"OTAU: CONTENT INFO - {str(item)} - - - - - - ")
print(f"Content Type: {content_info[0]}")
print(f"Bite Size: {content_info[1]}")
print(f"Updated Timestamp: {content_info[2]}")
print(f"Description: {content_info[3]}")
endpoint = f"/provision/download?id={str(item)}"
headers = {
'X-Exosite-CIK': token,
'Accept': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=utf-8',
#'Range': 'bytes=0-1000' # only used if downloading in chunks of a range of bytes at a time
}
conn.request('GET', endpoint, headers=headers)
r = conn.getresponse()
#print(f"STATUS: {str(r.status)}\nREASON: {r.reason}")
content_blob = r.read()
print(f"OTAU: CONTENT START - {str(item)} - - - - - - ")
print(content_blob.decode('UTF-8'))
print(f"OTAU: CONTENT END - {str(item)} - - - - - - ")
# WRITE FILE TO OS, MAKE AVAIABLE FOR UPDATE PROCESS
time.sleep(3)
update_otau_status({'version': manifest['version'],'status': 'DOWNLOAD_STEP' ,'message': ''})
time.sleep(3)
update_otau_status({'version': manifest['version'],'status': 'DOWNLOAD_SUCCESS' ,'message': ''})
time.sleep(3)
##
## Update Process
##
print(f"OTAU: Update Process Start")
update_otau_status({'version': manifest['version'],'status': 'INSTALL' ,'message': ''})
## <UPDATING FIRMWARE CODE HERE>
time.sleep(3)
update_otau_status({'version': manifest['version'],'status': 'INSTALL_STEP' ,'message': ''})
time.sleep(1)
update_otau_status({'version': manifest['version'],'status': 'INSTALL_SUCCESS' ,'message': ''})
time.sleep(3)
##
## Finish
##
print(f"OTAU: Update Process Completed")
update_otau_status({'version': manifest['version'],'status': 'INSTALLED_VERSION' ,'message': ''})
elif r.status == 304:
print("OTAU: Long Polling Time Out")
elif r.status==400:
print("OTAU: Bad Request")
data = r.read()
print(data)
break
conn.close()
print("OTAU: Application stopping")
conn.close()
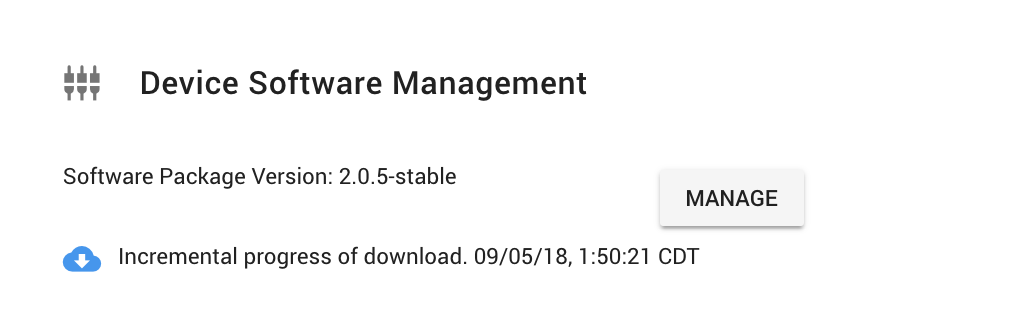
ExoSense End-user Experience¶
Users with Device Management and Device Software Package Management role permissions are able to apply the updates to the specific devices.
Once applied, devices will provide status updates